What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is the on-demand availability of computing resources like servers, storage, networking, software, analytics, and AI over the internet. It allows users to access resources from remote data centers instead of owing and managing the resources themselves. The service typically uses pay-as-you-go model which enables the users to only pay for what resources they use.
How does it work?
Cloud computing uses a network (like Internet, Intranet, Intercloud) to connect users to a cloud platform and deliver the resources to the client. The users (clients) rent computing services from the cloud platform according to their need and pay for what they use.
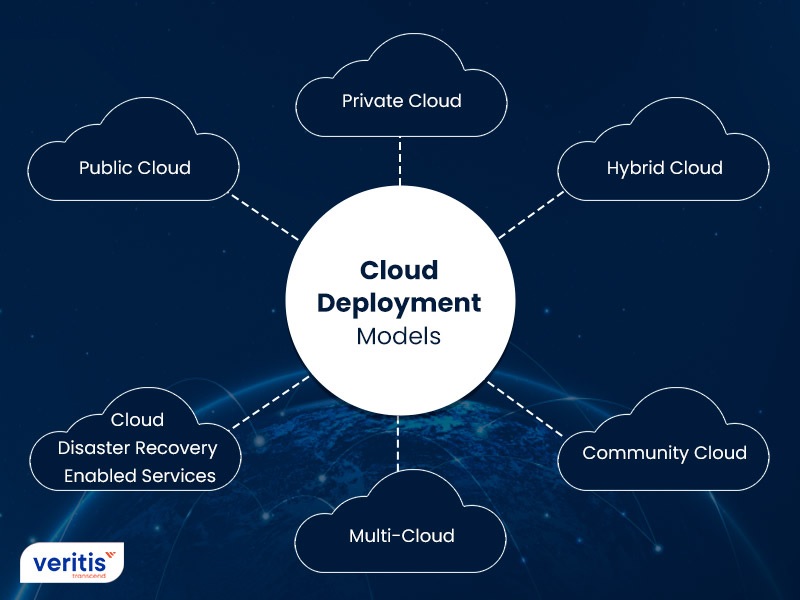
Types of cloud deployment models
- Public Cloud: It is owned and managed by a third-party cloud service providers (like Google and AWS) and delivers services over the internet. Its resources are shared among multiple users, making it cost-effective. It offers high scalability, minimal maintenance for users, and pay-as-you-go model.
- Private Cloud: It is built, managed, and owned by a single organization providing greater control over data and infrastructure. It can be hosted either on-premises or off-premises by a third-party provider. It enhances security and customization compared to public clouds.
- Hybrid Cloud: It combines public and private cloud environments into a single system. It allows data and applications to move between both environments as needed. This offers flexibility by allowing companies to store sensitive data on their private cloud and using public cloud for other applications to leverage their scalability features.
- Multi-cloud: It is an approach where an organization uses services from multiple cloud providers (public cloud) at the same time. It helps avoid reliance on a single vendor and improves reliability. Companies can choose the best services and pricing from each provider.
- Community Cloud: It is shared by multiple organizations that have similar requirements such as security, compliance, or objectives. It can be managed jointly by the organizations or by a third-party provider. This model allows cost sharing while enabling collaboration and controlled access among community members.
Types of cloud computing services
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): IaaS provides virtualized computing resources such as servers, storage, and networking over the internet. Users have control over operating systems and applications while the provider manages the physical infrastructure
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS offers a complete platform for developing, testing, and deploying applications. The provider manages hardware, operating systems, and runtime environments. Developers can focus on application development without worrying about infrastructure.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): SaaS delivers fully functional software applications through a web browser. The service provider handles maintenance, updates, and security. Users can access applications easily without installation or hardware management.
Benefits of cloud computing
- Cost Efficiency: Reduces the need for upfront hardware and maintenance costs. This allows resources to match demand efficiently without unnecessary resource allocation.
- Scalability & Flexibility: Resources can be scaled up or down easily based on demand. This ensures optimal performance without overprovisioning.
- Accessibility & Mobility: Data and applications can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection. This supports remote work and collaboration.
- Reliability & Availability: Cloud providers offer high uptime with data backup and disaster recovery. This minimizes downtime and data loss.
- Security: Advanced security features like encryption, firewalls, and regular updates are provided. This helps protect data from threats.
- Automatic Updates & Maintenance: Software updates and system maintenance are handled by the provider. This reduces the burden on internal IT teams.