A virtual machine (VM) is software that simulates a physical computer within another computer. It runs its own operating system and applications independently from the host system. Multiple virtual machines can run on a single physical machine, sharing its hardware resources, with the help of a hypervisor. A hypervisor manages virtual machines.
What is hypervisor?
A hypervisor is a software layer (also called a Virtual Machine Manager/Monitor, VMM) that lets a single physical computer host and run multiple virtual machines (VMs) simultaneously each with its own operating system. It allocates and manages the underlying hardware resources (CPU, memory, storage) among these VMs while keeping them isolated from one another.
Why do we need hypervisor?
We need a hypervisor because it enables efficient and flexible use of physical hardware by creating and managing multiple virtual machines on a single server. This loads to better resource utilization, reducing the number of physical machines required and lowering hardware, energy, and maintenance cost.
Hypervisors provide isolation and security between virtual machines. This makes systems easier to manage and test. They support features like scalability, portability, and rapid provisioning, which are essential for modern cloud computing and IT infrastructure. They also simplify disaster recovery and system management by allowing VMs to be migrated or replicated easily.
How does hypervisor work?
A hypervisor works by running directly on top of hardware or on top of host operating system. It abstracts the hardware resources like CPU, memory, storage, and network as well as creates and manages virtual machines, allocating resources to each VM as needed.
The hypervisor ensures insolation, so each VM runes independently with its own operating system. It also monitors and controls VM execution to maintain performance and security.
Types of hypervisor
1. Type-1 Hypervisor
- Type-1 hypervisor is also known as Bare-metal Hypervisor. It runs directly on physical hardware without a host OS and offers better performance and security.
- It is commonly used in data centers and cloud environments.
- e.g.: VMware ESXi, Microsoft Hyper-V
2. Type-2 Hypervisor
- Type-2 hypervisor is also known as Hosted Hypervisor. It runs on top of a host OS like a regular application and is easier to set up compared to type-1 hypervisor.
- It is mainly used for development, testing, and personal use.
- e.g.: VMware Workstation, Virtualbox
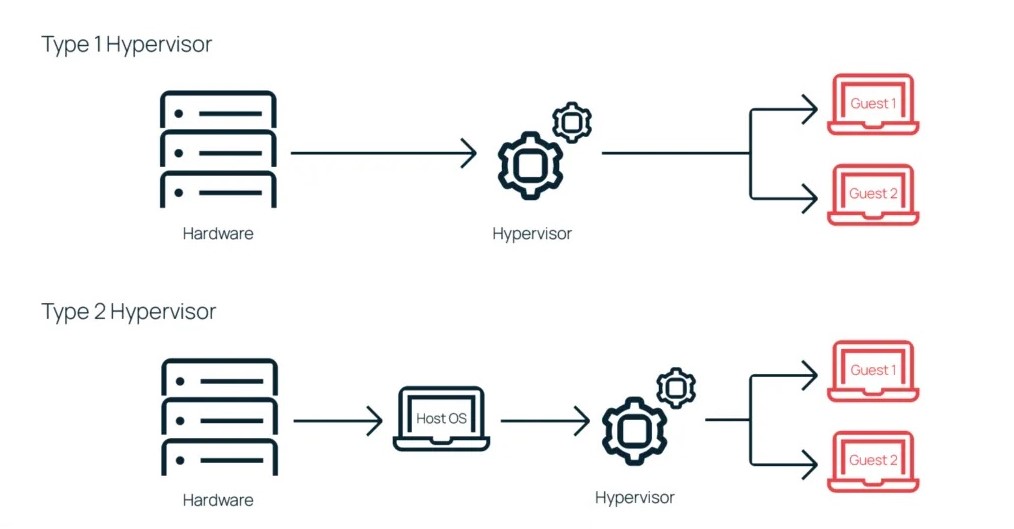
This image was taken from gigacloud
Benefits of hypervisor
- Efficient Resource Utilization: Runs multiple virtual machines on one physical server, maximizing CPU, memory, and storage usage.
- Cost Reduction: Fewer physical servers are needed, reducing hardware, power, cooling, and maintenance costs.
- Isolation & Security: Each virtual machine is isolated, so failures or security issues in one VM do not affect others.
- Flexibility & Scalability: Virtual machines can be created, modified, cloned, or scaled quickly to meet changing workload demands.
- High Availability & Disaster Recovery: Supports snapshots, backups, and live migration, enabling fast recovery and minimal downtime.